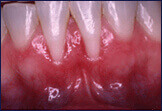
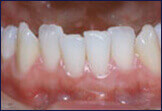
Soft Tissue Grafting

Gum grafts, also known as soft tissue grafts, are performed to increase the amount of gum tissue on teeth with recession. Recession of the gums (gingiva) can be caused by many factors, including heavy toothbrushing, clenching of the teeth, and/or incorrect alignment of the teeth.
The primary role of the gum tissue is to cover and protect the underlying jawbone that anchors the teeth. When the gums recede, that means that the bone that had covered the root is gone too.
So in actuality, a soft tissue graft is not just for cosmetics; a soft tissue graft helps prevent further gum recession and bone loss around the affected teeth.
Usually, a very small portion of gum tissue from the roof if the mouth is removed and then sutured in the area with gum recession. Both the roof of the mouth and the recession site will be numb, so you will not feel any pain or discomfort.
The periodontist will prescribe adequate medications to control any soreness and infection. After the first 24-48 hours, the soreness tends to dramatically subside. The sutures are removed after 1 week, and the soft tissue graft will continue to heal and blend with the surrounding gum tissue for the next few weeks.
Soft tissue grafts are a gentle, predictable method for treating teeth with gum recession with results that can last a lifetime.